Cloud computing is no longer an unfamiliar term for the financial industry. Over the last decade, the adoption of cloud technology has been increasing at an unprecedented pace. Research shows that cloud investment across banking had been growing at 30% annually and is predicted to to reach $411 billion by 2022. This trend has been more strongly reinforced by the pandemic for the demand of increased safe, secure, quick and convenient transactions. In this blog post, the Holland Fintech undercover team will explain the concept of cloud computing, analyze why this trend is gaining popularity and simultaneously point out potential risks that need to be taken into account.
What is Cloud Computing?
According to the definition given by Wikipedia, cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage (cloud storage) and computing power, without direct active management by the users.
How many types of cloud computing are there?
| Private Cloud | Public Cloud | Hybrid Cloud |
| The cloud services used by a single organization, which are not exposed to the public. A private cloud resides inside the organization and must be behind a firewall, so only the organization has access to it and can manage it. | The cloud services are exposed to the public and can be used by anyone. Virtualization is typically used to build the cloud services that are offered to the public. An example of a public cloud is Amazon Web Services (AWS) | The cloud services can be distributed among public and private clouds, where sensitive applications are kept inside the organization’s network (by using a private cloud), whereas other services can be hosted outside the organization’s network (by using a public cloud). Users can then interchangeably use private as well as public cloud services in every day operations. |
What are advantages and disadvantages of cloud-based payment systems?
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Cost efficiency Banking and financial institutions have to constantly renew facilities (e.g: hardwares) to ensure smooth services, protect proprietary data, and at the same time, maintain the largest capacity in case a high volumned project takes place. → Cloud technology lessens the complexity of renovating hardware infrastructure and removes the unnecessary maintenance cost by offering the ability to scale up and scale down automatically based on resource usage. | Internet connection Cloud relies 100% on the internet and having a strong internet is the most important requirement for cloud to function sufficiently. This might be an obstacle for companies which are either outsourced or located in developing countries or in remote areas where the system suffers from connection instability.
|
| Security and resiliency Banks and financial institutions have to maximize internet access for consumers, thus exposing their systems to cyber attacks. The system is manually monitored, making it slower and more difficult to detect non-permitted access → Cloud providers can substantially restrict human access to data to minimise risks such as human error. → Cloud is globally served from hundreds of data centers. Thus, it is quicker to detect penetration of unprotected systems by automated mechanisms. → Cloud providers also offer the functionality necessary to quickly move processes and data from one cloud provider to another, increasing the resiliency of financial institutions in the event of a disruption | Data removal/deletion Deleting entire data on cloud might be a little difficult because the data is not only stored in a single facility. While cloud offers backup and durability by keeping the data across multiple facilities, this feature could pose a challenge to completely remove the information from the storage infrastructure.
|
| Data analysis The ability to scale up on demand opens possibility for companies to hold a larger number of users, thereby being able to collect and analyze consumers’ data on a massive scale | Security threats Companies will share sensitive information to third-parties which are cloud computing service providers. Multiple users’ accounts are held on a software program which allocates cloud resources to customers as needed. This software could be hacked and the data could be authoritatively accessed. |
| Compliance The data analysis software will be insightful for financial institutions and regulators to take action on potential fraud and criminalities. | Limited control For public cloud, customers may have difficulty in controlling their deployments, which are completely managed by cloud service providers |
| Sustainability By saving a huge amount of energy, cloud technology lessens environmental impact, largely contributes to “green” finance and fulfil the goal organizations in improving ESG scores and reporting | Overreliance Different vendors offer different hosting platforms. Companies may face difficulties if they have to move to a new provider. During the transition phase, security attacks could happen due to insufficiently managed systems or inadequately protected databases. |
What do customers think about Cloud technology?
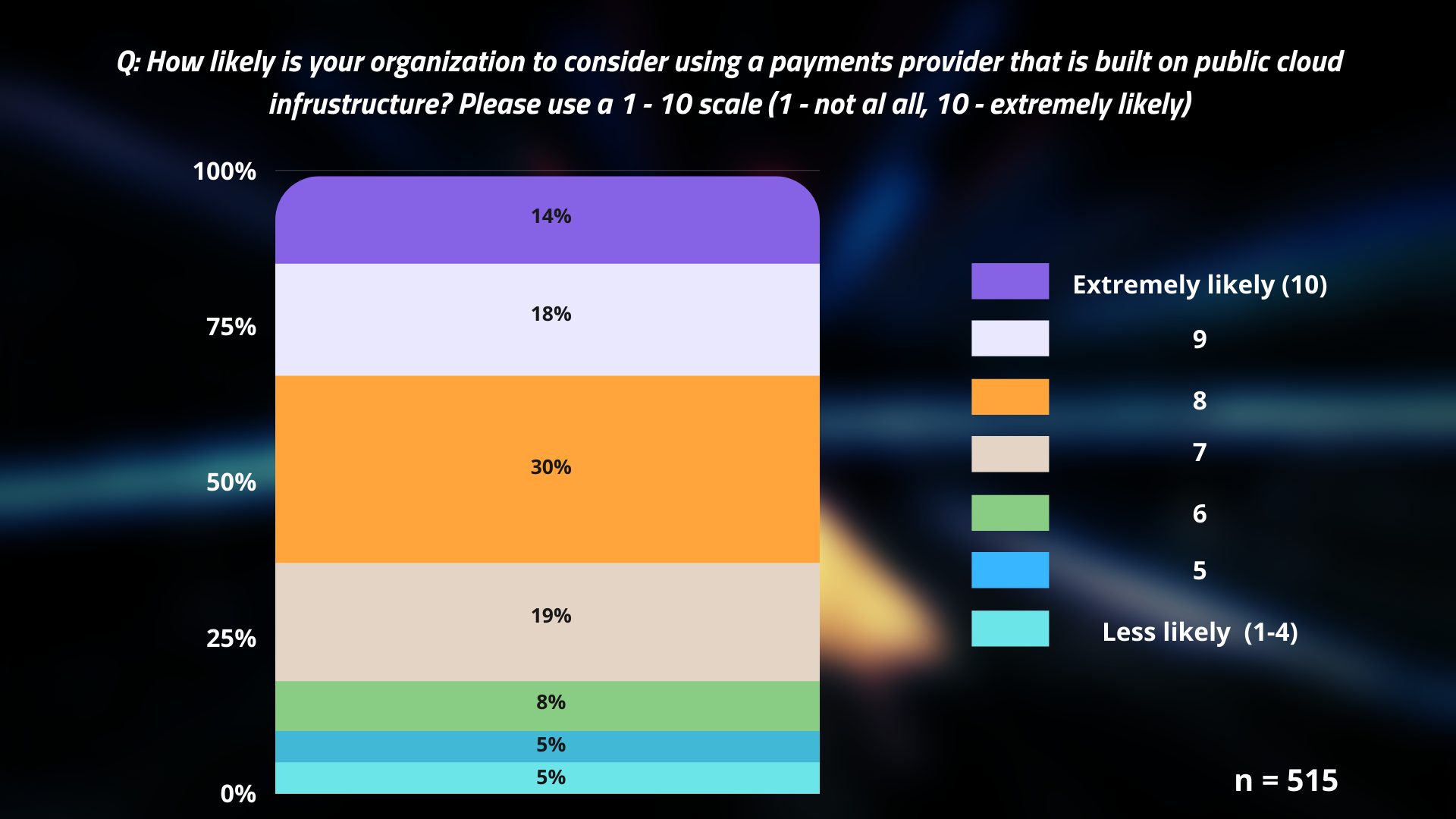
According to research conducted on 800 global merchants, when asked how likely their organizations are to consider using a payments provider that is built on a public cloud, more than half of the respondents are willing to adopt this technology, in which 30% chose “likely”, 18% chose “very likely” and 14% chose “extremely likely”.
Surprisingly, up to 75% of respondents are willing to pay a premium for improvements to their hosting and cloud service. The most desired improvements are guarantees of security (48.7% of respondents) and service performance (43.3%) with less interest in paying service providers to take on the operational management burden (27.9%).
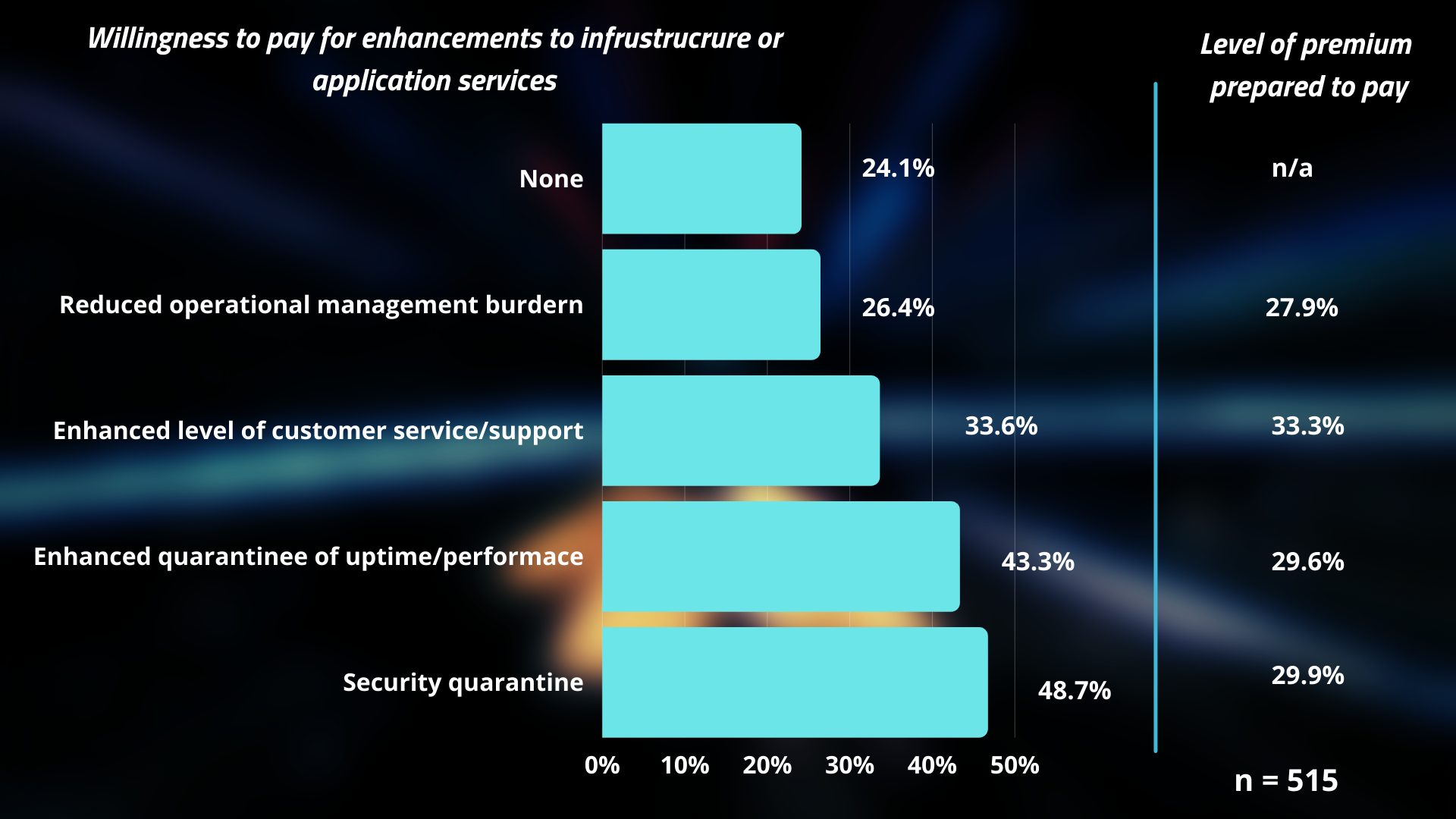
Findings imply that customers have high expectations of cloud services and place high hopes for the future that this technology will enhance their business performances. At the same time, these figures also pressurize cloud service providers to answer the question of how to meet their expectations for the above-mentioned categories such as security, financial performances, and customer support.


